Home > African Marke > Kenya
Time: Jun 17, 2016
AIDS Epidemic and Response
AIDS epidemic in the country
Number of people living with HIV | 1,400,000 [1,200,000 - 1,600,000] |
Adults aged 15 to 49 prevalence rate | 5.3% [4.7% - 6.1%] |
Adults aged 15 and up living with HIV | 1,200,000 [1,100,000 - 1,400,000] |
Women aged 15 and up living with HIV | 700,000 [620,000 - 810,000] |
Children aged 0 to 14 living with HIV | 160,000 [140,000 - 180,000] |
Deaths due to AIDS | 33,000 [25,000 - 45,000] |
Orphans due to AIDS aged 0 to 17 | 650,000 [480,000 - 1,100,000] |
Source: HIV and AIDS estimates (2014)[1] from UNAIDS Data
General description: Kenya has both a generalised and a concentrated epidemic, deeply rooted among the general population while there is also concentration of high prevalence among key populations.
HIV prevalence is higher among the general population in urban areas than those in rural areas. However, men in rural areas are more likely to be infected by HIV than men in urban areas (4.5% compared to 3.7%). Over time, the HIV prevalence in urban and rural areas has converged with only a modest different between the two.
Prevalence estimates by county shows the geographical variability of the HIV burden across the country. It is estimated that HIV prevalence ranges from a high 27.1% in Homa Bay County to below 0.2% in Wajir County. Ten counties have an estimated prevalence higher than the national average, while 7 counties have prevalence of less than 2%. This variability shows the need to design programmes that address the specific underlying issues in the counties.
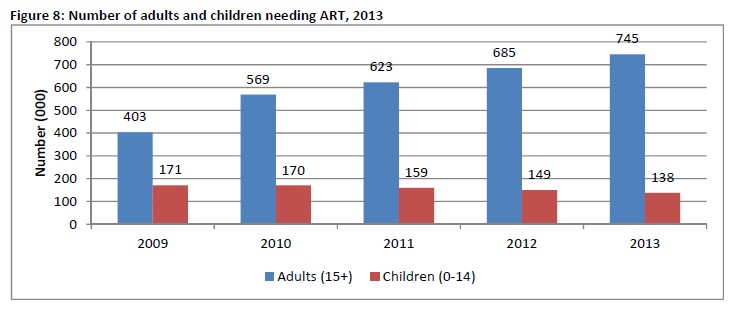
The number of adults in need of ART has been increasing while that of children has been declining in the last five years. In December 2013, PLHIV needing ART were estimated at about 880,000. Adults aged 15 years and above constituted 85% of the total of PLHIV in need of ART.
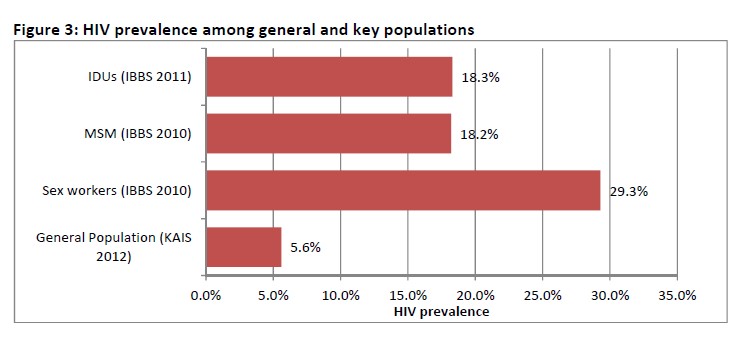
AIDS epidemic among key populations: Figure 3 shows the prevalence in the general populations and among three key populations in Kenya.
Female sex workers are a key population with an elevated HIV prevalence of about 29.3% compared to the national average (general population). However, only about 68% of the FSWs tested for HIV and know their results in the last 3 months. Eighty six percent of sex workers reported use of condom with their most recent client;
HIV prevalence among men having sex with men is almost three times more than the prevalence in the general population. About 18.2% of MSMs are living with HIV. The percentage of MSMs counselled and tested for HIV annually increased from a low of 35% in 2011 to 74% in 2013. However, condom use remains low although there has been an increase from 54.9% in 2011 to 68.8% in 2013;
The population of PWID is estimated at 18,327 and is concentrated in specific geographical areas particularly Nairobi and Mombasa. The Mode of HIV Transmission (MOT) study conducted in 2008 found that about 3.8% of new HIV infections occur among People Who Inject Drugs (PWIDs).
 |
National AIDS response
People who injecting drugs (PWIDs): Beginning 2008, the country initiated a programme to prevent HIV infections among the PWIDs mainly in Nairobi and Coast regions. Through this programme, about 271,941 needles and syringes were distributed in the past 12 months reaching about 2,000 PWIDs, which is about 135 needles and syringes per person per year. However, this programme reaches a limited number of people (about 15%) of the total estimated number of PWIDs.
Male circumcision: Kenya initiated Voluntary Medical Male Circumcision VMMC in 2008. Since then, the programme has been scaled up from about 8,000 VMMCs performed annually in 2008 to 190,000 in 2013. Over this five‐year period, about 670,000 VMMCs were performed against a target of 860,000; which means 77% achievement of the target. About 50% of the males circumcised were aged 15‐19 years and about 80% of the VMMCs were conducted in Nyanza region. The overall coverage of circumcision among men aged 15‐49 in the country is estimated at 91%. The highest increase of VMMC was in Nyanza region increased from 48% to 66% in 5 years.
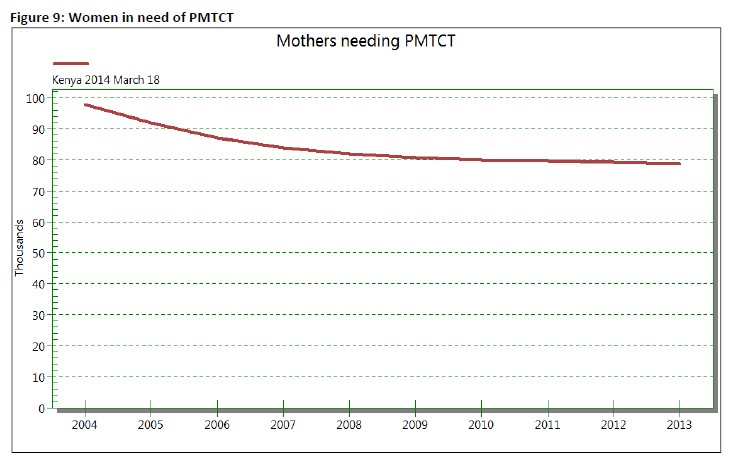
Maternal health & PMTCT: The coverage of pregnant women tested for HIV increased from 68.3% to 92.2% in 5 fears. This shows that Kenya has reached near universal testing for HIV of all women attending ANC. There were about 79,000 women needing PMTCT services annually over the last five years beginning 2009 while an average of 58,000 women were offered this service annually. A review of data on women in need and those accessing PMTCT shows an average of 76% coverage of this service. The PMTCT coverage declined from 86% in 2010 to 70% in 2013 largely due to increase in demand. The percentage of women or their infants given ARVs during breastfeeding to prevent HIV transmission over the last three years increased from 65% to 70.6%.
ARV & ART: Kenya has tremendously scaled up HIV treatment and care the last 10 years to each about 80% of those in need. From 2008 to date, Kenya has rapidly expanded the health system to provide ART services. Consequently, the eligible PLHIV on ART increased from 64% in 2008 to about 80% in 2013. The country also established and rapidly scaled up paediatric ART from 16% in 2008 to 43% in 2013.
[1] http://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/kenya/